Forest use
Forest use means to utilize its resources, i.e. timber, ground cover products, Christmas trees, whole plants or their parts suitable for the needs of pharmaceutical industry; it is also extracting minerals and many others. The foresters make forests accessible to the public, however in a way which ensures their sustainability.
The size of timber harvest is determined by the forest management plan prepared for each forest district for a 10-year period. It ensures that the size of timber logging is kept not only within the limits of the productive function of forest but it also systematically increases the so called growing stock, ie. timber remaining in the forest. To summarize, foresters’ management ensures the sustainability of forests and the possibility of their biological reproduction.
The volume of timber harvest is decided by the allowable cut determined by forest management plan for each forest district. It is the amount of timber allowed to be logged in selected forest stands located in a designated area in a period of 10 years scheduled by the plan. Owing to this, the allowable cut is lower than the actual increment of timber in the same period, so the growing stock increases systematically (in Poland about 55% of the increment is harvested). It is estimated that the current abundance of Polish forests is over 2.4 milliard cubic meters of timber).
The methods of timber harvesting:
- Felling – removing mature stands from forest; the basic aim of felling is to rebuild and restore stands;
- Tending cuts (clearing and thinning) – removing from forest a part of trees presumed to be unwanted and harmful to other trees and valuable parts of stands;
- Unplanned cuts – they are the result of natural disasters in the forests.
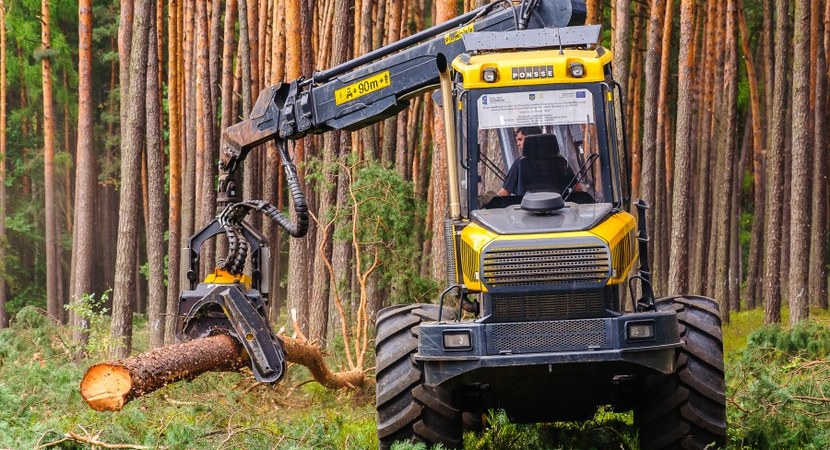
The State Forests make use of forest machinery to more and more greater extent. In the forest there work more machines such as harvesters and forwarders. They increase the ergonomics and effectiveness of harvesting. This machinery is the property of the State Forests units or forest service providers working for the State Forests.
The forests gifts also include eagerly picked mushrooms and the number of the edible species growing in Polish forests is over 1000.
In the forest we also gather the fruit of: common billbery (also blue whortleberry), lingonberry, blackberry, raspberry, dog rose, hawthorn, rowan (commonly known also as mountain-ash), cranberry, black elder, hazel tree and many more, almost impossible to be all enlisted here. It is worth remembering that the edible forest products are allowed to be picked by everybody for their own needs, of course one must keep in mind not to damage mycelium, plants and other elements of natural environment where they exist.
Many of us associate forest with Christmas trees. Every year, about 200 thousand Christmas trees coming from the State Forests are supplied to Polish homes. They come either from special Christmas tree plantations or tending cuts made in spruce stands. Apart from spruce the more popular becomes pine which is harvested in tending cuts made in nurseries and sapling stands.